This story is a reprint from Kyowa Kirin Annual Report 2022.
We are actively working to conserve the environment for future generations. As part of this commitment, we aim to decarbonize our company, including the value chain.
Environmental Management
Having incorporated priority environmental issues from the perspective of their impact on the sustainability of society and on the Group’s business in its FY2021–2025 Medium Term Business Plan, Kyowa Kirin is setting targets for each fiscal year and implementing measures accordingly. In particular, we have positioned climate change mitigation and adaptation and water resource management as core environmental issues. As well as our annual targets, we have set medium- and long-term targets, developing a range of measures to achieve these.
We have established and are operating a governance structure for Kyowa Kirin’s environmental management. The Executive Vice President has been appointed as its chief executive officer.
In our daily environmental management activities, we operate all of our domestic plants and research laboratories in accordance with the ISO 14001 environmental management system.
Addressing climate change
The Kirin Group, of which Kyowa Kirin is a member, has formulated the Kirin Group Environmental Vision 2050. In its vision, the Kirin Group has set a goal of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions in its entire value chain by 2050 as a “Society that has overcome climate change,” a society in 2050 that we want to create together regarding climate change.
Kyowa Kirin has also adopted the target of reducing CO2 emissions in 2030 by 55% from the 2019 level. As specific commitments related to climate change, we are committed to “Promoting early reduction of CO2 emissions” through “Energy conservation” and “Expansion of renewable energy” including capital investment, and “Promoting energy conversion.” Having created a road map for achieving the 2030 target, we have also set a short-term target (FY2024 CO2 emissions: 51% reduction compared with 2019). Utilizing the Kirin Group as a network, we will contribute to the realization of this vision by actively developing climate change measures that leverage our business characteristics.
To promote the use of renewable energy Kyowa Kirin has been promoting the introduction of solar power generation equipment since 2011. As of the end of FY2022, such equipment is in operation at the Tokyo and Fuji research parks and at the Ube and Takasaki plants. In March 2023, we install and operate a large-scale solar power generation facility (1.47 MW) at the Ube Plant using an on-site power purchase agreement (PPA) model and are thereby planning to accelerate the reduction of CO2 emissions.

In the meantime, we have been gradually introducing RE100-compliant renewable energy at the Takasaki Plant and Fuji Research Park since 2020, switching 100% of the electricity at each plant to renewable energy. In April 2023, we introduce this system at the Ube Plant, and switch 100% of the electricity used at this plant to RE100-compliant renewable energy. By introducing these renewable energy projects, of the approximately 70,900,000 kWh of annual power consumption of the Kyowa Kirin Group, approximately 60,300,000 kWh will be switched to renewable energy with zero CO2 emissions, and the plan is for the Group’s annual CO2 emissions to be reduced by approximately 53% (27,300 t).*1 In 2021, RE100-compliant renewable energy was also introduced for the electricity (100%) of the head office.*2
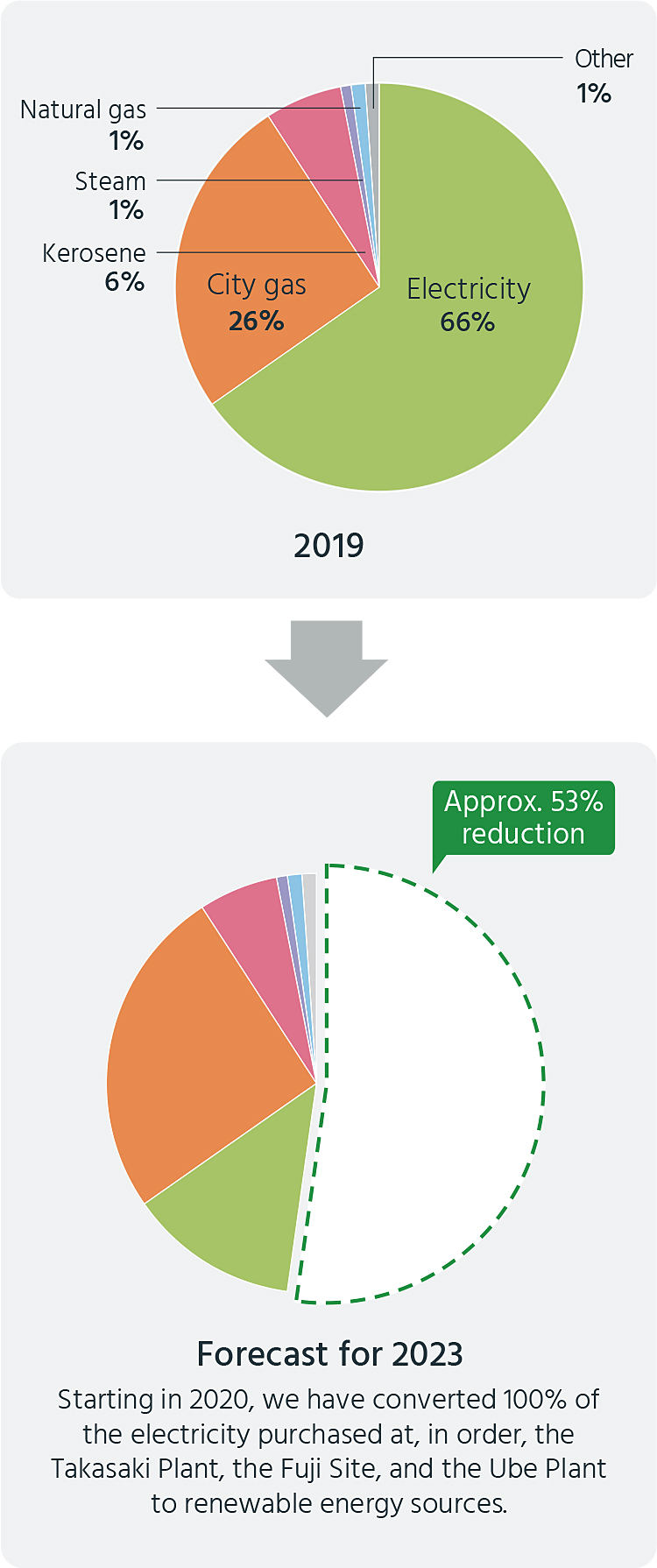

Going forward, the plan is for us to have switched to 100% renewable energy at our major business locations in Japan by 2025, and to all of our group business locations, including overseas sites and domestic branch offices, by 2030. In addition, we are considering the introduction of solar power generation facilities at our domestic plants and research laboratories as well as at our overseas plant.
Each plant and research laboratory*3 sets its own energy intensity reduction targets for a single year, implementing measures to improve production efficiency. Although we implemented various measures to improve production efficiency, unit energy consumption in FY2022 was 2.2% higher than the previous year due to the effects of production facility enhancements and production volume increases.
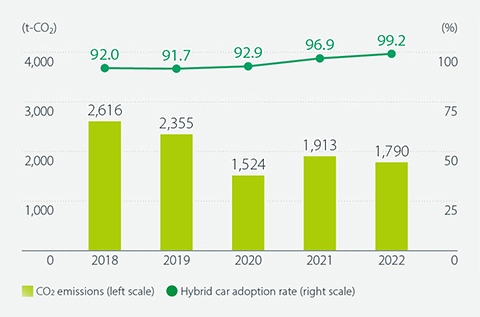
Also working to reduce CO2 emissions from our sales vehicles, since 2009 we have been promoting the introduction of hybrid cars for our sales vehicles (company cars) in Japan. Since FY2019, all newly introduced sales vehicles have been hybrid cars, and the hybrid car adoption rate had reached 99.2% by the end of FY2022. In addition, new information provision activities such as web-based interviews, information sessions and lectures are increasing, contributing to the reduction of CO2 emissions.
Water resources management
Kyowa Kirin conducts water risk assessments (such as water shortage/water stress, flooding, and water pollution of water sources risk assessments by WRI Aqueduct and WWF Water Risk Filter) at each plant in Japan and overseas.
As a result of the assessments, we identified that the Ube Plant has a higher risk of flooding due to droughts and storm surges and that at Kyowa Kirin China Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Shanghai) the risks of water shortages and flooding were greater than at other plants. In the latest local flooding simulation published by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, it is assumed that the Takasaki Plant would suffer flood damage.
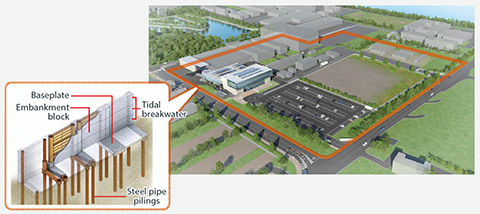
In response to these results, alongside soft measures such as reviewing or formulating plant BCPs for large-scale natural disasters, we are also implementing hard measures such as flood prevention measures at facilities to avoid or minimize these risks.
Under the Kirin Group Environmental Vision 2050, Kyowa Kirin is working to conserve water and protect water resources in accordance with the Kyowa Kirin Group Environmental Policy. In 2021, we reviewed our previous 2030 water consumption (water withdrawal) reduction target and set a new 2030 water withdrawal reduction target of a 40% reduction from 2019 levels. We are also setting short-term targets to achieve the 2030 target. To reduce water withdrawal, we will systematically decommission and reorganize facilities while making effective investments in equipment such air-cooled refrigeration units. As of the end of FY2022, we have achieved a 33% reduction from the 2019 level*1 against our 2030 water withdrawal reduction target. Furthermore, to improve the efficiency of water use, each year, each plant and research laboratory sets and manages its own water consumption intensity. In 2022, our water consumption intensity was 9.7% lower*3 than the previous year.
Biodiversity
At Kyowa Kirin, we are using our procurement activities to help protect the world’s forests. Specifically, we have adopted FSC®-certified products*4 for materials such as company envelopes, company brochures, and cardboard product packaging. In accordance with the Kirin Group Action Plan for Sustainable Use of Biological Resources, which was revised in 2021, we continue to study applications for FSC®-certified products. In addition to expanding their use for domestic product packaging cardboard boxes, we are considering using them for materials such as product inner boxes. We have also begun considering the use of FSC®-certified products overseas, at business sites and for products.

As part of its activities to preserve ecosystems and ensure biodiversity, Kyowa Kirin has been working to protect water resources through its engagement in the Kirin Group’s water-source preservation project since FY2007. The Takasaki and Ube plants carry out weeding, planting and tree thinning to create forest areas that provide water resources. In addition, for the seventh year running, Kirin Holdings Company, Limited has been recognized as the highest Water Security A List company by CDP, an international non-profit organization that provides an environmental data disclosure system. CDP praised the Kirin Group, of which Kyowa Kirin is a member, for its efforts in protecting water resources, evaluating river basin water risks at manufacturing sites, and for formulating and implementing strategies that reflect those risks.

Kyowa Kirin business sites also work with various local communities to preserve ecosystems, including releasing young amago trout into rivers, or protecting grasslands of Akiyoshidai in Yamaguchi Prefecture. The Fuji site continues to collaborate with local government on activities such as Shizuoka Prefecture’s River Friendship Program, which organizes cleanups of local rivers, and a campaign to clean up trash from areas around Mount Fuji. Through these activities, we will continue to support local communities and raise awareness of the importance of preserving the beauty of the natural environment and protecting biodiversity.

In our research, development, and manufacturing of pharmaceutical products, we have established an in-house committee to ensure compliance with the Act on the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biological Diversity through Regulations on the Use of Living Modified Organisms (“the Cartagena Act”) and to conduct appropriate management. At the 2022 Genetically Modified Organism Committee meeting, we shared the results of audits that focused on countermeasures against leaks of experimental applications in each department.
The Kirin Group is advancing a range of initiatives in this area, including the Kirin Group Declaration of Support for Biodiversity Conservation, formulated in 2010, and the Kirin Group’s Guidelines on Sustainable Sourcing of Biological Resources, formulated in 2013.
- *1Calculated based on FY2019 data for Kyowa Kirin Group’s plants and research laboratories in Japan and overseas.
- *2Otemachi Financial City Grand Cube, where Kyowa Kirin’s head office is located, has adopted RE100-compliant electricity derived from renewable energy sources.
- *3Kyowa Kirin Group plants and research laboratories in Japan and plants overseas.
- *4Kyowa Kirin has obtained an FSC® promotion license (FSC® N003037).
Responding to the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
Since announcing our endorsement of the TCFD recommendations in 2021, Kyowa Kirin has identified the risks and opportunities that climate change poses to our business, as well as the impacts of these risks and opportunities. We have organized our findings into four areas: governance, strategy, risk/opportunity management, and indicators and targets in line with TCFD recommendations.
Governance (relating to environmental issues)
Issues related to risks and opportunities in climate change, as well as environmental activity policies and results are positioned as important matters in the Group’s environmental management. These issues are reported, deliberated upon, and decided by the CSR Committee, which is chaired by the Representative Director and Executive Vice President, who has the highest responsibility for overall environmental management. The content of these discussions is reported to the Board of Directors. In addition, from FY2020 we put in place a TCFD Study Team within the CSR Management Department, which is responsible for the environmental management control function. This team studies the identification and evaluation of climate change-related risks and opportunities and our response to them. We are addressing climate-related issues as part of management strategy by regularly reviewing the risks and opportunities that have been identified and reporting them to and having them brought up by the CSR Committee.
Strategy
We aim to achieve a world in which the average temperature increase is limited to 1.5°C or less, as outlined in the Paris Agreement. We are reviewing our climate change response based on the results of our scenario analysis of climate change-related risks and opportunities and also in the context of the Kirin Group Environmental Vision 2050. We are incorporating these findings into our business strategy and advancing measures accordingly.
As mitigation measures, to support the achievement of net-zero greenhouse gas emissions throughout the value chain by 2050, we have not only upwardly revised our 2030 CO2 reduction target to a level corresponding to the Science-Based Target (SBT) 1.5°C target* but also established a roadmap for achieving this target and set short-term targets. Having incorporated targets (CO2 emission reduction achievement rate, renewable energy introduction rate, 1% reduction in energy intensity compared with the previous year, etc.) for each fiscal year in the FY2021-2025 Medium Term Business Plan, we are promoting measures, such as the early introduction and expansion of renewable energy, energy conservation, and energy conversion, and responding to the risks associated with the transition to a decarbonized society.
As an adaptive measure, we will formulate a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) for large-scale natural disasters. This will address the impact on global production activities arising from flooding of plant and research laboratory premises. We respond to physical risks by implementing flooding prevention measures and capital investment as required. Going forward, we will continue to minimize risk by assessing and addressing the impact throughout our supply chain.
On the other hand, an increase in the number of hay fever sufferers had led to expectations of an opportunity for the allergy drug market. However, we believe the actual impact on sales revenue will be limited. Recognizing that this will form an important point in future business strategies, we will continue to consider new developments in this field to meet medical needs based on our management philosophy.
- *Science-based corporate greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets consistent with the Paris Agreement levels
Risk/opportunity management
To identify risks and opportunities, we comprehensively assess-based on scenario analysis for each risk and opportunity - the expected timing and probability of occurrence, the scope and magnitude of impact, and the nature of countermeasures. We manage these risks and opportunities by identifying those that have a significant impact on business, that involve a high degree of social responsibility, or have a high probability of occurrence. We monitor and manage, on a quarterly basis, our measures to address the risks we have identified.
Metrics and targets
In 2021, we set a new 2030 CO2 emissions reduction target of 55% reduction from 2019 levels. This is based on the SBT 1.5°C target. In addition to creating a roadmap for achieving these new targets, we have set short-term targets (2024 CO2 emissions: 51% reduction compared with 2019). Incorporated into our FY2021-2025 Medium Term Business Plan, we are setting and managing annual targets for each fiscal year, while studying and developing measures to achieve them.
In addition, the Kirin Group has set a goal, based on the Kirin Group Environmental Vision 2050, of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions for the entire value chain by 2050. As medium-term targets, the Group has upwardly revised its greenhouse gas reduction target to a 50% reduction in Scope 1 + Scope 2 and a 30% reduction in Scope 3 by 2030 compared to 2019 (approved for the SBT 1.5°C target). A target of 100% renewable energy sources for electricity consumption has been set for 2040 (RE100 member). Kyowa Kirin has developed its 2030 targets and measures in alignment with these medium- and long-term goals of the Kirin Group.
The greenhouse gas emissions in the Kyowa Kirin Group’s value chain (Scope 3) are calculated by dividing them into 15 categories in accordance with the Ministry of the Environment’s guidelines, which are consistent with the GHG Protocol. To achieve the Kirin Group’s goal of net-zero greenhouse gas emissions for the entire value chain by 2050, we will continue to work on reducing Scope 3 emissions.
Analysis of risks, opportunities and financial impact related to climate change
You can see this table by scrolling horizontally.
| Scenario classification | Climate change-related drivers with impact assessment | Potential impact | Change through response (resilience) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition risk | Policy and regulations | Carbon pricing (decarbonization, emissions trading schemes) | Risk:Small | ±0 |
| Tighter CO2 emission regulations | Opportunity:Slight | Opportunity:Small | ||
| Population/economy/geopolitics | Population growth in emerging economies/economic globalization | ±0 | ±0 | |
| Community | Changing social values | Risk:Slight | ±0 | |
| Physical risk | Increase in average temperature and change in rainfall pattern (acute) | Extreme temperature rises | Risk:Small | Opportunity:Small |
| Increased torrential rains, typhoons, and floods | Risk:Large | Risk:Slight | ||
| Increase in average temperature, changes in rainfall pattern (chronic) | Changes in hay fever patients | Opportunity:Medium | Opportunity:Medium | |
| Increased energy consumption due to increased air conditioning load | Risk:Small | Opportunity:Small | ||
- Achieve 2030 target early and reduce CO2 emissions
- Review workplace BCPs for major natural disasters
- Disaster preparedness of facilities